-
June 8, 632
 Mohammed, the founder of Islam and unifier of Arabia, dies, and Abu Bakr, his father-in-law, becomes first Caliph during Rashidun Caliphate, the term comprising the first four caliphs in Islam's history
Mohammed, the founder of Islam and unifier of Arabia, dies, and Abu Bakr, his father-in-law, becomes first Caliph during Rashidun Caliphate, the term comprising the first four caliphs in Islam's history -
August 22, 634Abu Bakr, successor of Mohammed and first Caliph, dies; Umar, a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, becomes the second Caliph
-
634Byzantium city of Damascus is captured by the Muslims
-
August 15, 636At the Battle at Yarmuk Islamic forces under Khalid ibn al-Walid beat a Byzantine army under Emperor Heraclius and gain control of Syria and Palestine
-
638Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab gives an assurance of safety to the people of Jerusalem
-
639Islamic armies invade Egypt
-
641Founding of Fustat near Cairo, the first capital of Egypt under muslim rule
-
November 8, 641
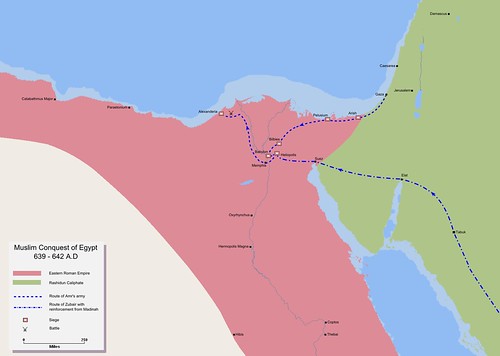 After a fourteen month siege Muslims take Alexandria from Byzantine Empire completing the conquests of Egypt
After a fourteen month siege Muslims take Alexandria from Byzantine Empire completing the conquests of Egypt -
642Muslim Arabs invade Armenia and capture Dvin, its principal town, slaughtered 12,000 of its inhabitants
-
642Islamic forces decisively defeat Persians at the battle of Nihawand completing the conquest of the Sassanid Empire
-
642The library at Alexandria, Egypt, disappears completely
-
November 7, 644Caliph Umar, one of the most powerful caliphs of the Rashidun Caliphate, dies after being stabbed by Pirouz Nahavandi while the morning prayer three days before
-
December 14, 644Uthman ibn Affan, one of the companions of Islamic prophet Muhammad, is appointed the third Caliph by council
-
650Zayd ibn Thabit, the personal scribe of Muhammad, with a group of some scribes complete the compilation of Muhammad's revelations into one work called the Koran
-
650Babylonian Talmud, a compilation of documents compiled over the period of Late Antiquity, is finalized in Mesopotamia
-
651
 Sassanid king Yazdegerd III is assassinated by local miller while his attempt to flee from Merv, marking end of Sassanid Dynasty in Persia
Sassanid king Yazdegerd III is assassinated by local miller while his attempt to flee from Merv, marking end of Sassanid Dynasty in Persia -
June 20, 656
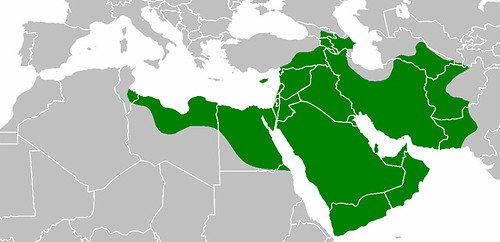 Caliph Uthman ibn Affan is assassinated, thus Ali becomes caliph
Caliph Uthman ibn Affan is assassinated, thus Ali becomes caliph -
November 7, 656
 Rashidun Caliphate beats rebel forces at the Battle of the Camel, the first battle of First Islamic Civil War
Rashidun Caliphate beats rebel forces at the Battle of the Camel, the first battle of First Islamic Civil War -
July 26, 657
 Battle of Siffin occurs between Governor of Syria Muawiyah I and Rashidun Caliphate during the first Muslim civil war
Battle of Siffin occurs between Governor of Syria Muawiyah I and Rashidun Caliphate during the first Muslim civil war -
January 31, 661Muawiyah I, the governor of Levant, founds Umayyad Dynasty in Damascus, after Ali, the last Caliph of Rashidun Caliphate dies, wounded by poison-coated sword while praying in mosque in Iraq three days before, which marks the split of Islam into Sunni and Shi'a branches
Tuesday, December 27, 2016
Rashidun Caliphate
Labels:
Abu Bakr,
Ali,
Asia,
Battle at Yarmuk,
Battle of the Camel,
Cairo,
Caliphs,
Islam,
Koran,
Medina,
Muawiyah I,
Muhammad,
Muslim Conquests,
Pirouz Nahavandi,
Rashidun Caliphate,
Umar,
Uthman ibn Affan,
Yazdegerd III
Wednesday, October 5, 2016
Seleucus I Nicator
-
358 BC
 Seleucus I Nicator, one of the Diadochi and the founder of the Seleucid Empire, is born in family of Philip II of Macedon's generals in Europos, the northern part of Macedonia
Seleucus I Nicator, one of the Diadochi and the founder of the Seleucid Empire, is born in family of Philip II of Macedon's generals in Europos, the northern part of Macedonia -
May, 326 BC
 Macedonian army under Alexander the Great defeats Indian king Porus at the battle of The Hydaspes River in Punjab, modern-day Pakistan, expanding Alexandrian Empire to its maximum extent
Macedonian army under Alexander the Great defeats Indian king Porus at the battle of The Hydaspes River in Punjab, modern-day Pakistan, expanding Alexandrian Empire to its maximum extent -
324 BC, FebruarySeleucus marries Apama, the Persian princess Apama, at the great marriage ceremony at Susa, arranged by Alexander of Macedon
-
June 13, 323 BC
 Alexander the Great dies of fever after a feast in Babylon, which causes wars of the Diadochoi, his generals and friends, in the Empire
Alexander the Great dies of fever after a feast in Babylon, which causes wars of the Diadochoi, his generals and friends, in the Empire -
321 BCAfter assassination of Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's empire, during The First War of the Diadochi, and partition of the empire between Perdiccas' opponents, Seleucus is appointed Satrap of Babylon under the new regent Antipater
-
312 BC
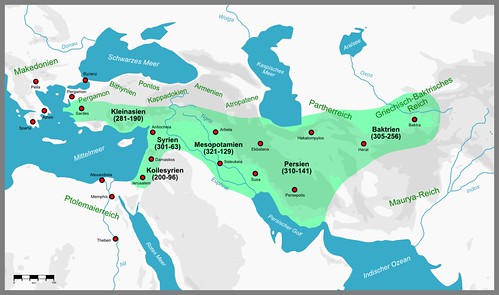 Being forced to flee Babylon by Antigonus, Seleucus I Nicator returns to Babylon with the support of Ptolemy I Soter and formally establishes Seleucid Empire in Mesopotamia
Being forced to flee Babylon by Antigonus, Seleucus I Nicator returns to Babylon with the support of Ptolemy I Soter and formally establishes Seleucid Empire in Mesopotamia -
305 BCSeleucus I Nicator, the Basileus of the Seleucid Empire, founds the city of Seleucia on the Tigris and makes it new capital of the empire, which eventually depopulates Babylon
-
305 BC
 Chandragupta Maurya, the first emperor of Mauryan Empire, seizes the satrapies of Paropanisadai, Aria, Arachosia and Gedrosia from Seleucus I Nicator, the Macedonian satrap of Babylonia, in return for 500 elephants
Chandragupta Maurya, the first emperor of Mauryan Empire, seizes the satrapies of Paropanisadai, Aria, Arachosia and Gedrosia from Seleucus I Nicator, the Macedonian satrap of Babylonia, in return for 500 elephants -
301 BC
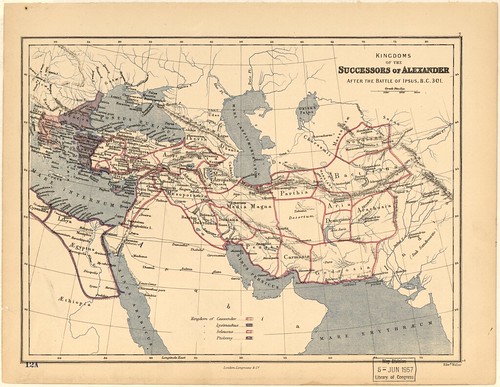 Antigonus I Monophthalmus, a Macedonian general and satrap under Alexander the Great, is defeated and killed by the united forces of Seleucus and Lysimachus at battle of Ipsus, ending the Fourth War of the Diadochi and confirming dissolution of Alexander's empire
Antigonus I Monophthalmus, a Macedonian general and satrap under Alexander the Great, is defeated and killed by the united forces of Seleucus and Lysimachus at battle of Ipsus, ending the Fourth War of the Diadochi and confirming dissolution of Alexander's empire -
281 BC
 Seleucus I Nicator invades Asia Minor and defeats Lysimachus, the King of Macedon and his last rival, in the Battle of Corupedium in Lydia, which leaves him the only living contemporary of Alexander the Great
Seleucus I Nicator invades Asia Minor and defeats Lysimachus, the King of Macedon and his last rival, in the Battle of Corupedium in Lydia, which leaves him the only living contemporary of Alexander the Great -
281 BC
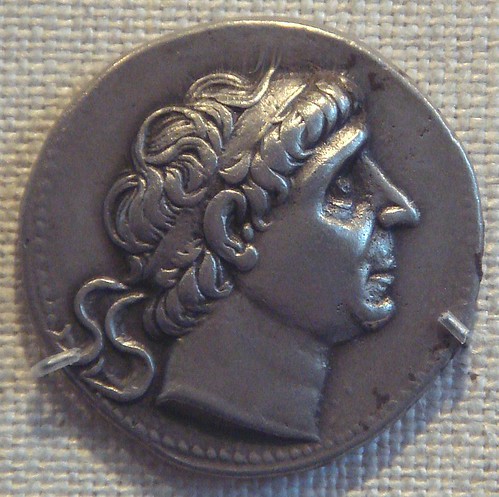 Seleucus I Nicator, the founder of the Seleucid Empire, is assassinated by the King of Macedon Ptolemy Ceraunus, and is succeeded by his son Antiochus I as ruler of the Seleucid empire
Seleucus I Nicator, the founder of the Seleucid Empire, is assassinated by the King of Macedon Ptolemy Ceraunus, and is succeeded by his son Antiochus I as ruler of the Seleucid empire
Saturday, September 17, 2016
Jean-Jacques Dessalines
-
September 20, 1758
 Jean-Jacques Dessalines, the first ruler of an independent Haiti, is born and named after his owner Jean-Jacques Duclos, in Guinea
Jean-Jacques Dessalines, the first ruler of an independent Haiti, is born and named after his owner Jean-Jacques Duclos, in Guinea -
August 22, 1791
 Haitian Revolution, the only slave revolt which led to the founding of a state, begins in the French colony of Saint-Domingue
Haitian Revolution, the only slave revolt which led to the founding of a state, begins in the French colony of Saint-Domingue -
May 6, 1794
 After the French declared an end to slavery, Toussaint Louverture, Haitian rebel leader, ends his alliance with the Iberian monarchy and embraces the French Republicans
After the French declared an end to slavery, Toussaint Louverture, Haitian rebel leader, ends his alliance with the Iberian monarchy and embraces the French Republicans -
1801Dessalines cruelly supresses an insurrection in the north led by Toussaint Louverture's nephew, General Moyse
-
March 22, 1802
 After a 20-day siege Dessalines and his 1,300 men are forced to abandon strategically important Crete-a-Pierrot fort and go into the Cahos Mountains through the enemy lines being largely intact
After a 20-day siege Dessalines and his 1,300 men are forced to abandon strategically important Crete-a-Pierrot fort and go into the Cahos Mountains through the enemy lines being largely intact -
1802, OctoberAfter the betrayal and capture of Toussaint Louverture and re-establishment slavery in Guadeloupe by France, Dessalines becomes the leader of the revolution
-
November 18, 1803Jean-Jacques Dessalines, Haitian rebel leader, leads his army to decisive victory over the French at the Battle of Vertieres, the last major battle of the the Haitian Revolution
-
January 1, 1804
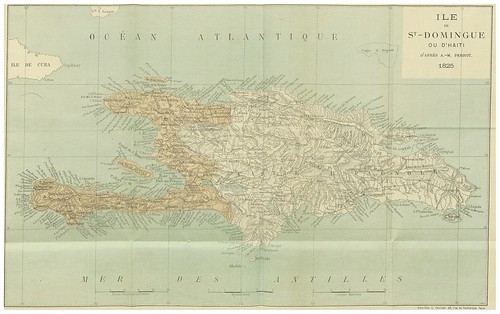 Jean-Jacques Dessalines declares independence from France and proclaims the Republic of Haiti, making it the only nation in the world established as a result of a successful slave revolt
Jean-Jacques Dessalines declares independence from France and proclaims the Republic of Haiti, making it the only nation in the world established as a result of a successful slave revolt -
April 20, 1804
 Jean-Jacques Dessalines, Haitian rebel leader, commands 1804 Haiti Massacre of the French at town of Cape Francois, during which the white Haitians were practically eradicated
Jean-Jacques Dessalines, Haitian rebel leader, commands 1804 Haiti Massacre of the French at town of Cape Francois, during which the white Haitians were practically eradicated -
October 8, 1804
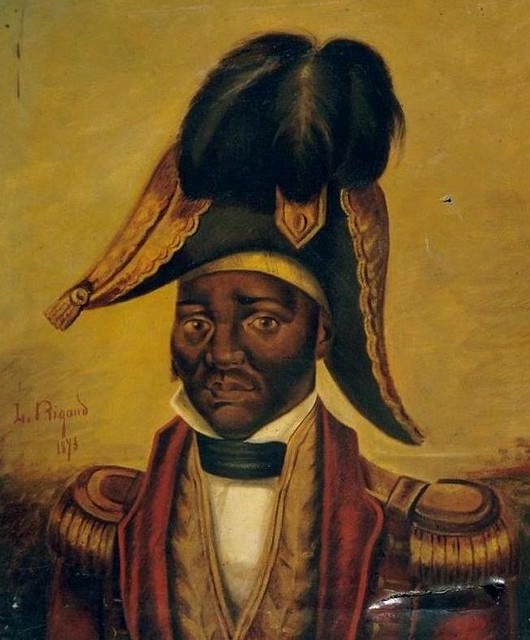 Jean-Jacques Dessalines, Governor-General of Haiti, crowns himself James I, Emperor of Haiti with the right to name his successor, in the city of Le Cap
Jean-Jacques Dessalines, Governor-General of Haiti, crowns himself James I, Emperor of Haiti with the right to name his successor, in the city of Le Cap -
May 20, 1805The Imperial Constitution of Haiti, which names Dessalines emperor for life with the right to name his successor, is released
-
October 17, 1806Jean-Jacques Dessalines, the Emperor of Haiti, is assassinated by members of his administration after a meeting to negotiate the future of the young nation
Saturday, February 13, 2016
Hussite Wars
-
July 6, 1415
 Jan Hus, Bohemian religious reformer who spoken out against Church corruption, is burned as a heretic at the stake at Constance, Germany
Jan Hus, Bohemian religious reformer who spoken out against Church corruption, is burned as a heretic at the stake at Constance, Germany -
September 1, 1415The nobles of Bohemia and Moravia send the protestatio Bohemorum to the Council of Constance, which strongly condemns the execution of Hus
-
July 30, 1419
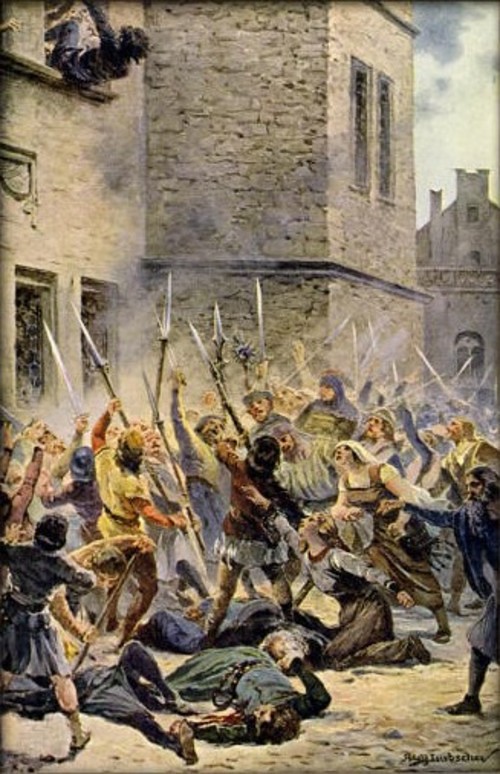 The group of the followers of Jan Hus threw the judge, the burgomaster, and some thirteen council members out of the window of the New Town Hall in Prague triggering Hussite Wars in central Europe
The group of the followers of Jan Hus threw the judge, the burgomaster, and some thirteen council members out of the window of the New Town Hall in Prague triggering Hussite Wars in central Europe -
March 1, 1420Pope Martin I calls for the first of five crusades against the Hussieten
-
March 25, 1420
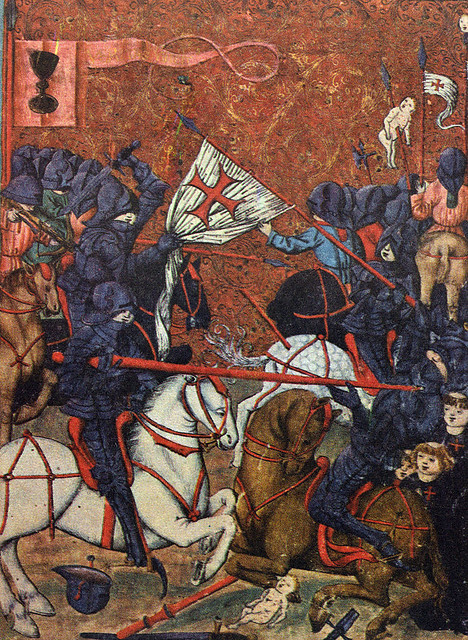 Jan ЕЅiѕka, Czech general and Hussite leader, defeats the Catholic forces at the Battle of Sudomer in southern Bohemia, the first battle of the Hussite wars
Jan ЕЅiѕka, Czech general and Hussite leader, defeats the Catholic forces at the Battle of Sudomer in southern Bohemia, the first battle of the Hussite wars -
July 14, 1420
 Hussite forces under command of Jan ЕЅiѕka defeat the forces of Emperor Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor at the Battle of Vitkov Hill, a part of the first anti-Hussite crusade, on the edge of the city of Prague
Hussite forces under command of Jan ЕЅiѕka defeat the forces of Emperor Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor at the Battle of Vitkov Hill, a part of the first anti-Hussite crusade, on the edge of the city of Prague -
1422Vytautas, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, accepts the crown of Bohemia, offered by Jan ЕЅiѕka, with the condition that the Hussites reunite with the Catholic Church
-
August 14, 1431Hussite forces led by Prokop the Great defeat a large army of crusaders under Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg, at the Battle of Domaiѕlice during the fifth anti-Hussite crusade
-
May 30, 1434
 An army of Utraquists and Catholics, called the Bohemian League, defeat the radical Taborites and Orphans, led by Prokop the Great and Prokop the Lesser, who both fell in the battle of of Lipany, which marks the end of the Hussite wars
An army of Utraquists and Catholics, called the Bohemian League, defeat the radical Taborites and Orphans, led by Prokop the Great and Prokop the Lesser, who both fell in the battle of of Lipany, which marks the end of the Hussite wars -
July 5, 1436An agreement ending the Hussite wars and establishing the Utraquist creed in Bohemia is signed by King Sigismund, by the Hussite delegates, and by the representatives of the Roman Catholic Church at Jihlava, in Moravia
Egyptian Obelisks
-
1950 BC
 The earliest Egyptian obelisk still in its original position is erected by Senusret I at Al-Matariyyah in Heliopolis, near Cairo
The earliest Egyptian obelisk still in its original position is erected by Senusret I at Al-Matariyyah in Heliopolis, near Cairo -
1450 BC
 The largest ancient Egyptian obelisk, weighing nearly 1,200 tons, is abandoned unfinished at the stone quarries in Aswan due to cracks in the granite
The largest ancient Egyptian obelisk, weighing nearly 1,200 tons, is abandoned unfinished at the stone quarries in Aswan due to cracks in the granite -
1200 BC
 Two red granite monolithic obelisks of different height are erected at the entrance of the Temple of Luxor emphasizing the heights and distance from the wall
Two red granite monolithic obelisks of different height are erected at the entrance of the Temple of Luxor emphasizing the heights and distance from the wall -
10 BC
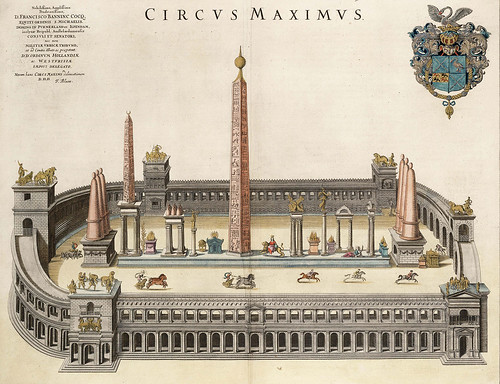 Flaminio Obelisk, one of the thirteen ancient obelisks in Rome, is taken from the Temple of Sun in Heliopolis, Egypt, and placed on the spina of the Circus Maximus by command of Augustus
Flaminio Obelisk, one of the thirteen ancient obelisks in Rome, is taken from the Temple of Sun in Heliopolis, Egypt, and placed on the spina of the Circus Maximus by command of Augustus -
37
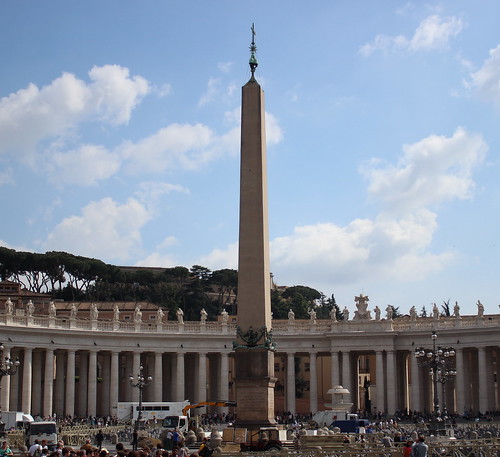 An Egyptian obelisk of red granite, today known as Vatican Obelisk, is moved from the Julian Forum of Alexandria to Rome and placed at the Circus of Nero by order of Emperor Caligula
An Egyptian obelisk of red granite, today known as Vatican Obelisk, is moved from the Julian Forum of Alexandria to Rome and placed at the Circus of Nero by order of Emperor Caligula -
1586
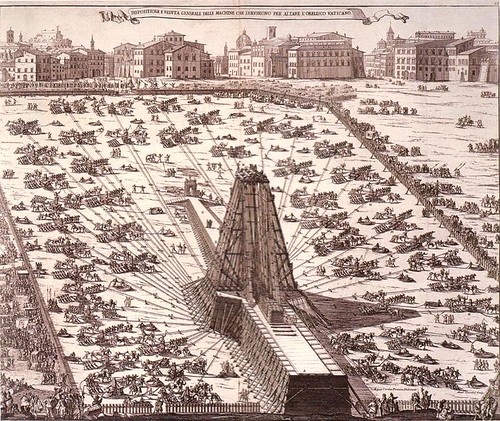 An obelisk that has been brought from Egypt to Rome by the emperor Caligula in AD 37 is erected by Italian architect Domenico Fontana at Saint Peter's Square in Rome
An obelisk that has been brought from Egypt to Rome by the emperor Caligula in AD 37 is erected by Italian architect Domenico Fontana at Saint Peter's Square in Rome -
1829
 The Obelisk of Luxor, a gift of the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, is transported to the Place de la Concorde in Paris
The Obelisk of Luxor, a gift of the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali, is transported to the Place de la Concorde in Paris -
September 21, 1878
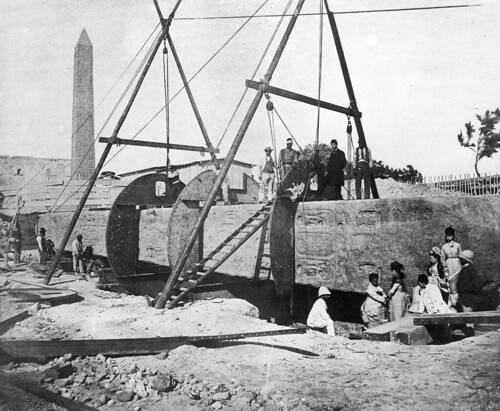 The red granite obelisk of Alexandria, known as Cleopatra's Needle, is erected upright at a public park on the Victoria Embankment, London
The red granite obelisk of Alexandria, known as Cleopatra's Needle, is erected upright at a public park on the Victoria Embankment, London -
February 22, 1881
 Cleopatra's Needle, a red granite Egyptian obelisk, made during the reign of pharaoh Thutmose III, is erected in Central Park, New York
Cleopatra's Needle, a red granite Egyptian obelisk, made during the reign of pharaoh Thutmose III, is erected in Central Park, New York
Labels:
Ancient Egypt,
Art,
Augustus,
Central Park,
Circus of Nero,
Cleopatra's Needle,
Egyptian Obelisks,
Flaminio Obelisk,
London,
Luxor,
Luxor Obelisk,
New York,
Obelisks,
Place de la Concorde,
Rome,
Sculpture
Saturday, January 23, 2016
Twenty-seventh Century BC
-
 Maize is domesticated in the Tehuacan Valley in Mesoamerica
Maize is domesticated in the Tehuacan Valley in Mesoamerica -
2700 BC В± 300
 One of the earliest known civilizations in the Aegean world, the Minoan civilization, rise on the island of Crete beginning the period of flourishing
One of the earliest known civilizations in the Aegean world, the Minoan civilization, rise on the island of Crete beginning the period of flourishing -
2700 BC
 Minoan Civilization ancient palace city Knossos reach 80,000 inhabitants
Minoan Civilization ancient palace city Knossos reach 80,000 inhabitants -
2700 BC
 Preservation of fish and poultry by drying and salting is invented in Egypt
Preservation of fish and poultry by drying and salting is invented in Egypt -
2700 BCMerit-Ptah, an early physician in ancient Egypt, becomes the world's first named woman in medicine and all of science
-
2686 BC
 Nebka, an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, begins to rule in Ancient Egypt, starting Third Dynasty of Egypt and the Old Kingdom
Nebka, an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, begins to rule in Ancient Egypt, starting Third Dynasty of Egypt and the Old Kingdom -
2675 BC
 Aga of Kish, the last king in the first Dynasty of Kish, is defeated by Gilgamesh of Uruk, the fifth king of that city, marking start of Uruk hegemony in Sumer
Aga of Kish, the last king in the first Dynasty of Kish, is defeated by Gilgamesh of Uruk, the fifth king of that city, marking start of Uruk hegemony in Sumer -
2650 BC
 The first step pyramid in Egypt is built for pharaoh Djoser at Saqqara by his vizier Imhotep, the first known architect
The first step pyramid in Egypt is built for pharaoh Djoser at Saqqara by his vizier Imhotep, the first known architect -
2650 BC
 Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors period in China, the first period in history of ancient China, characterized by semi-mythological rulers and considered as demigods and wise characters, begins
Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors period in China, the first period in history of ancient China, characterized by semi-mythological rulers and considered as demigods and wise characters, begins -
2650 BC
 The ancient city of Harappa in modern-day Pakistan, one of the largest metropolises of ancient world with superior urban planning and sewage systems, begins to flourish during urbanization in the Indus Valley civilization
The ancient city of Harappa in modern-day Pakistan, one of the largest metropolises of ancient world with superior urban planning and sewage systems, begins to flourish during urbanization in the Indus Valley civilization -
2620 BC
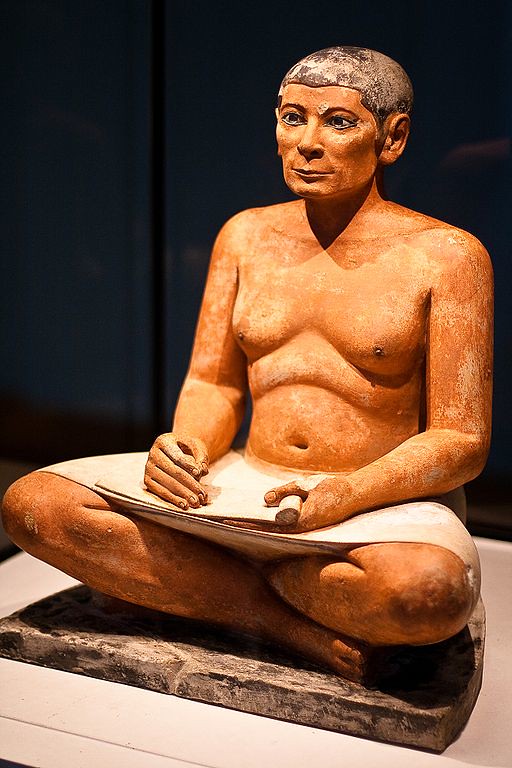 Seated Scribe, an Egyptian painted limestone realistic statue representing a figure of a seated scribe at work, is made
Seated Scribe, an Egyptian painted limestone realistic statue representing a figure of a seated scribe at work, is made -
2613 BC
 Sneferu, builder of three survived pyramids in Egypt, founds the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, following his father pharaoh Huni
Sneferu, builder of three survived pyramids in Egypt, founds the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, following his father pharaoh Huni
Labels:
Ancient Egypt,
Elam,
Fish,
Food,
Maize,
Minoan Civilization
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)